This blog is a part of my journey “Embarking on the AWS Solution Architect Associate SAA-CO3 Certification Journey”
Databases
Choosing the Right Database
- We have a lot of managed databases on AWS to choose from
- Questions to choose the right database based on your architecture:
- Read-heavy, write-heavy, or balanced workload? Throughput needs? Will it change, does it need to scale or fluctuate during the day?
- How much data to store and for how long? Will it grow? Average object size? How are they accessed?
- Data durability? Source of truth for the data ?
- Latency requirements? Concurrent users?
- Data model? How will you query the data? Joins? Structured? Semi-Structured?
- Strong schema? More flexibility? Reporting? Search? RDBMS / NoSQL?
- License costs? Switch to Cloud Native DB such as Aurora
Database Types
- RDBMS (= SQL / OLTP): RDS, Aurora – great for joins
- NoSQL database – no joins, no SQL : DynamoDB (~JSON), ElastiCache (key / value pairs), Neptune (graphs), DocumentDB (for MongoDB), Keyspaces (for Apache Cassandra)
- Object Store: S3 (for big objects) / Glacier (for backups / archives)
- Data Warehouse (= SQL Analytics / BI): Redshift (OLAP), Athena, EMR
- Search: OpenSearch (JSON) – free text, unstructured searches
- Graphs: Amazon Neptune – displays relationships between data
- Ledger: Amazon Quantum Ledger Database
- Time series: Amazon Timestream
Amazon RDS
- RDS stands for Relational Database Service
- It’s a managed DB service for DB use SQL as a query language.
- It allows you to create databases in the cloud that are managed by AWS
- Postgres
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Aurora (AWS Proprietary database)
Advantage over deploying DB on EC2
- RDS is a managed service
- Automated provisioning, OS patching
- Continuous backups and restore to specific timestamp (Point in Time Restore)
- Monitoring dashboards
- Read replicas for improved read performance
- Multi AZ setup for DR (Disaster Recovery)
- Maintenance windows for upgrades
- Scaling capability (vertical and horizontal)
- Storage backed by EBS (gp2 or io1)
- BUT you can’t SSH into your instances
RDS-Storage Auto Scaling
- Helps you increase storage on your RDS DB instance dynamically
- When RDS detects you are running out of free database storage, it scales automatically
- Avoid manually scaling your database storage
- You have to set Maximum Storage Threshold (maximum limit for DB storage)
- Automatically modify storage if:
- Free storage is less than 10% of allocated storage
- Low-storage lasts at least 5 minutes
- 6 hours have passed since last modification
- Useful for applications with unpredictable workloads
- Supports all RDS database engines (MariaDB, MySQL )
RDS Read Replicas for read scalability
- Up to 15 Read Replicas
- Within AZ, Cross AZ or Cross Region
- Replication is ASYNC, so reads are eventually consistent.
- Replicas can be promoted to their own DB.
- Applications must update the connection string to leverage read replicas
- Use Cases
- You want to run a reporting application to run some analytics.
- Network Cost
- In AWS there’s a network cost when data goes from one AZ to another
- For RDS Read Replicas within the same region, you don’t pay that fee
RDS Multi AZ – Disaster Recovery
- SYNC replication
- One DNS name – automatic app failover to standby
- Increase availability
- Failover in case of loss of AZ, loss of network, instance or storage failure
- No manual intervention in apps
- Not used for scaling
RDS Custom
- Managed Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server Database with OS and database customization.
- RDS: Automates setup, operation, and scaling of database in AWS.
- Custom: access to the underlying database and OS so you can
- Configure settings
- Install patches
- Enable native features
- Access the underlying EC2 Instance using SSH or SSM Session Manager
- De-activate Automation Mode to perform your customization, better to take a DB snapshot before
- RDS vs. RDS Custom
- RDS: entire database and the OS to be managed by AWS
- RDS Custom: full admin access to the underlying OS and the database
RDS Backups
- Automated backups
- Daily full backup of the database (during the backup window)
- Transaction logs are backed-up by RDS every 5 minutes
- ability to restore to any point in time (from oldest backup to 5 minutes ago)
- 1 to 35 days of retention, set 0 to disable automated backups
- Manual DB Snapshots
- Manually triggered by the user
- Retention of backup for as long as you want
RDS Restore
- Restoring a RDS / Aurora backup or a snapshot creates a new database
- Restoring MySQL RDS database from S3
- Create a backup of your on-premises database
- Store it on Amazon S3 (object storage)
- Restore the backup file onto a new RDS instance running MySQL
Amazon RDS Proxy
- Fully managed database proxy for RDS
- Allows apps to pool and share DB connections established with the database
- Improving database efficiency by reducing the stress on database resources (e.g., CPU, RAM) and minimize open connections (and timeouts)
- Serverless, autoscaling, highly available (multi-AZ)
- Reduced RDS & Aurora failover time by up 66%
- Supports RDS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, MS SQL Server) and Aurora (MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- No code changes required for most apps
- Enforce IAM Authentication for DB, and securely store credentials in AWS Secrets Manager
- RDS Proxy is never publicly accessible (must be accessed from VPC)
Amazon RDS – Summary
- Managed PostgreSQL / MySQL / Oracle / SQL Server / MariaDB / Custom
- Provisioned RDS Instance Size and EBS Volume Type & Size
- Auto-scaling capability for Storage
- Support for Read Replicas and Multi AZ
- Security through IAM, Security Groups, KMS , SSL in transit
- Automated Backup with Point in time restore feature (up to 35 days)
- Manual DB Snapshot for longer-term recovery
- Managed and Scheduled maintenance (with downtime)
- Support for IAM Authentication, integration with Secrets Manager
- RDS Custom for access to and customize the underlying instance (Oracle & SQL Server)
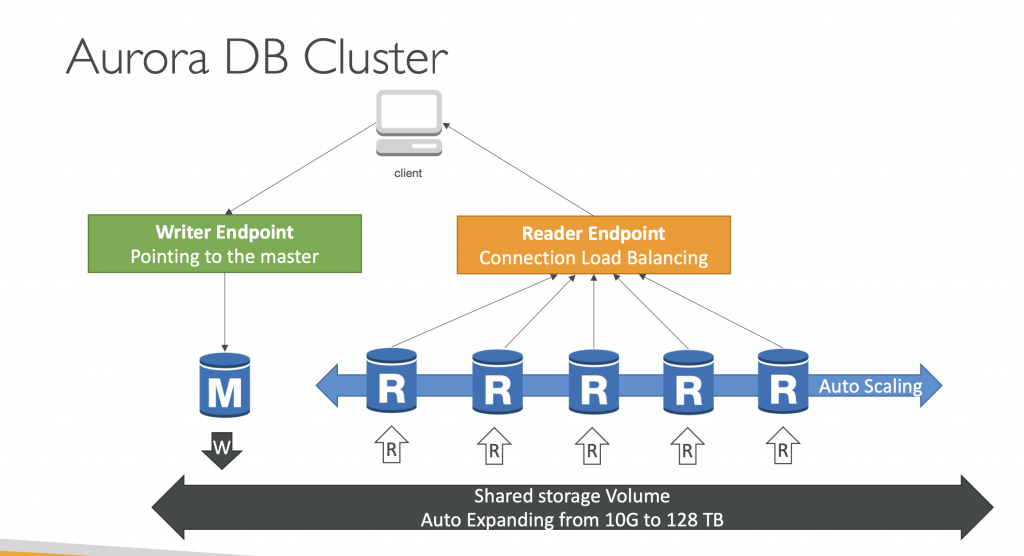
Amazon Aurora
- Aurora is a proprietary technology from AWS (not open sourced)
- Postgres and MySQL are both supported as Aurora DB (that means your drivers will work as if Aurora was a Postgres or MySQL database)
- Aurora is “AWS cloud optimized” and claims 5x performance improvement over MySQL on RDS, over 3x the performance of Postgres on RDS
- Aurora storage automatically grows in increments of 10GB, up to 128 TB.
- Aurora can have up to 15 replicas and the replication process is faster than MySQL (sub 10 ms replica lag)
- Failover in Aurora is instantaneous. It’s HA (High Availability) native.
- Aurora costs more than RDS (20% more) – but is more efficient
Aurora High Availability and Read Scaling
- 6 copies of your data across 3 AZ:
- 4 copies out of 6 needed for writes
- 3 copies out of 6 need for reads
- Self healing with peer-to-peer replication
- Storage is striped across 100s of volumes
- One Aurora Instance takes writes (master)
- Automated failover for master in less than 30 seconds
- Master + up to 15 Aurora Read Replicas serve reads
- Support for Cross Region Replication
Features of Aurora
- Automatic fail-over
- Backup and Recovery
- Isolation and security
- Industry compliance
- Push-button scaling
- Automated Patching with Zero Downtime
- Advanced Monitoring
- Routine Maintenance
- Backtrack: restore data at any point of time without using backups
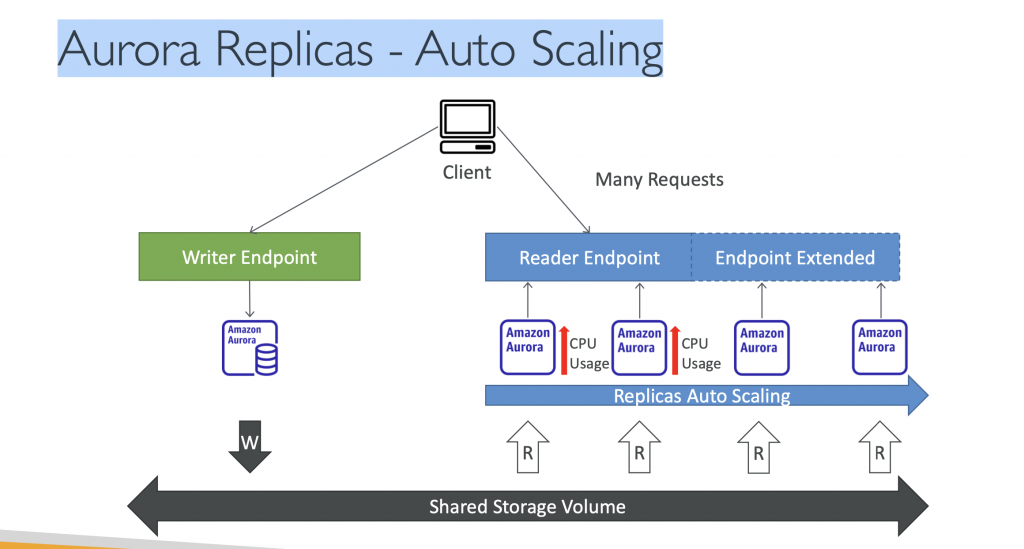
Aurora Replicas – Auto Scaling
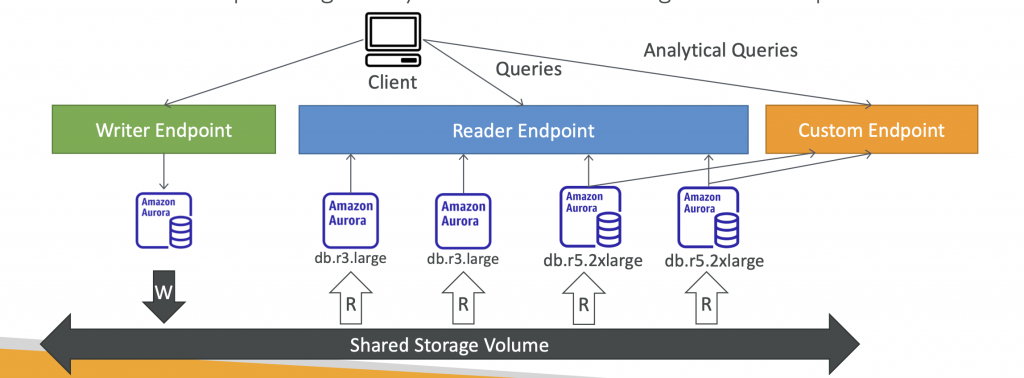
Aurora – Custom Endpoints
- Define a subset of Aurora Instances as a Custom Endpoint
- Example: Run analytical queries on specific replicas
- The Reader Endpoint is generally not used after defining Custom Endpoints
Aurora Serverless
- Automated database instantiation and auto- scaling based on actual usage
- Good for infrequent, intermittent or unpredictable workloads
- No capacity planning needed
- Pay per second, can be more cost-effective
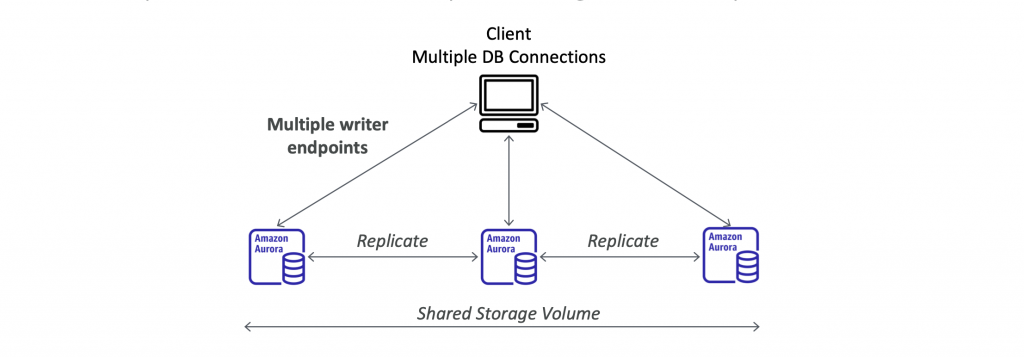
Aurora Multi-Master
- In case you want continuous write availability for the writer nodes
- Every node does R/W – vs promoting a Read Replica as the new master
Global Aurora
Aurora Cross Region Read Replicas:
- Useful for disaster recovery
- Simple to put in place
Aurora Global Database (recommended):
- 1 Primary Region (read / write)
- Up to 5 secondary (read-only) regions, replication lag is less than 1 second
- Up to 16 Read Replicas per secondary region
- Helps for decreasing latency
- Promoting another region (for disaster recovery) has an RTO of < 1 minute
- Typical cross-region replication takes less than 1 second
Aurora Machine Learning
- Enables you to add ML-based predictions to your applications via SQL
- Simple, optimized, and secure integration between Aurora and AWS ML services
- Supported services
- Amazon SageMaker (use with any ML model)
- Amazon Comprehend (for sentiment analysis)
- You don’t need to have ML experience
- Use cases: fraud detection, ads targeting, sentiment analysis, product recommendations
Aurora Backups
- Automated backups
- 1 to 35 days (cannot be disabled)
- point-in-time recovery in that timeframe
- Manual DB Snapshots
- Manually triggered by the user
- Retention of backup for as long as you want
Aurora Database Cloning
- Create a new Aurora DB Cluster from an existing one
- Faster than snapshot & restore
- Uses copy-on-write protocol
- Initially, the new DB cluster uses the same data volume as the original DB cluster (fast and efficient – no copying is needed)
- When updates are made to the new DB cluster data, then additional storage is allocated and data is copied to be separated
- Very fast & cost-effective
- Useful to create a “staging” database from a “production” database without impacting the production database
RDS & Aurora Security
- At-rest encryption:
- Database master & replicas encryption using AWS KMS – must be defined as launch time
- If the master is not encrypted, the read replicas cannot be encrypted
- To encrypt an un-encrypted database, go through a DB snapshot & restore as encrypted
- In-flight encryption: TLS-ready by default, use the AWS TLS root certificates client-side
- IAM Authentication: IAM roles to connect to your database (instead of username/pw)
- Security Groups: Control Network access to your RDS / Aurora DB
- No SSH available except on RDS Custom
- Audit Logs can be enabled and sent to CloudWatch Logs for longer retention
Amazon Aurora – Summary
- Compatible API for PostgreSQL/MySQL, separation of storage and compute
- Storage: data is stored in 6 replicas, across 3 AZ–highly available, self-healing, auto-scaling
- Compute: Cluster of DB Instance across multiple AZ, auto-scaling of Read Replicas
- Cluster: Custom endpoints for writer and reader DB instances
- Same security / monitoring / maintenance features as RDS
- Know the backup & restore options for Aurora
- Aurora Serverless – for unpredictable / intermittent workloads, no capacity planning
- Aurora Multi-Master – for continuous writes failover (high write availability)
- Aurora Global: up to 16 DB Read Instances in each region, < 1 second storage replication
- Aurora Machine Learning: perform ML using SageMaker & Comprehend on Aurora
- Aurora Database Cloning: new cluster from existing one, faster than restoring a snapshot
- Use case: same as RDS, but with less maintenance / more flexibility / more performance / more features
Amazon ElastiCache
- The same way RDS is to get managed Relational Databases
- ElastiCache is to get managed Redis or Memcached
- Caches are in-memory databases with really high performance, low latency
- Helps reduce load off of databases for read intensive workloads
- Helps make your application stateless
- AWS takes care of OS maintenance / patching, optimizations, setup, configuration, monitoring, failure recovery and backups
- Use cases
- DB cache
- Session store
ElastiCache – Redis vs Memcached
| REDIS | MEMCACHED |
| Multi AZ with Auto-Failover | Multi-node for partitioning of data (sharding) |
| Read Replicas to scale reads and have high availability | No high availability (replication) |
| Data Durability using AOF persistence | Non persistent |
| Backup and restore features | No backup and restore |
| Supports Sets and Sorted Sets | Multi-threaded architecture |
ElastiCache – Cache Security
- ElastiCache supports IAM Authentication for Redis
- IAM policies on ElastiCache are only used for AWS API-level security
- Redis AUTH
- You can set a “password/token” when you create a Redis cluster
- This is an extra level of security for your cache (on top of security groups)
- Support SSL in flight encryption
- Memcached
- Supports SASL-based authentication (advanced)
Amazon ElastiCache – Summary
- Managed Redis / Memcached (similar offering as RDS, but for caches)
- In-memory data store, sub-millisecond latency
- Select an ElastiCache instance type (e.g., cache.m6g.large)
- Support for Clustering (Redis) and Multi AZ, Read Replicas (sharding)
- Security through IAM, Security Groups, KMS, Redis Auth
- Backup / Snapshot / Point in time restore feature
- Managed and Scheduled maintenance
- Requires some application code changes to be leveraged
Amazon DynamoDB
- Fully managed, highly available with replication across multiple AZs
- NoSQL database – not a relational database – with transaction support
- Scales to massive workloads, distributed database
- Millions of requests per seconds, trillions of row, 100s of TB of storage
- Fast and consistent in performance (single-digit millisecond)
- Integrated with IAM for security, authorization and administration
- Low cost and auto-scaling capabilities
- No maintenance or patching, always available
- Standard & Infrequent Access (IA) Table Class
DynamoDB – Basics
- DynamoDB is made of Tables
- Each table has a Primary Key (must be decided at creation time)
- Each table can have an infinite number of items (= rows)
- Each item has attributes (can be added over time – can be null)
- Maximum size of an item is 400KB
- Data types supported are:
- Scalar Types – String, Number, Binary, Boolean, Null
- Document Types – List, Map
- Set Types – String Set, Number Set, Binary Set
Read/Write Capacity Modes
- Control how you manage your table’s capacity (read/write throughput)
- Provisioned Mode (default)
- You specify the number of reads/writes per second
- You need to plan capacity beforehand
- Pay for provisioned Read Capacity Units (RCU) & Write Capacity Units (WCU)
- Possibility to add auto-scaling mode for RCU & WCU
- On-Demand Mode
- Read/writes automatically scale up/down with your workloads
- No capacity planning needed
- Pay for what you use, more expensive
- Great for unpredictable workloads, steep sudden spikes
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
- Fully-managed, highly available, seamless in- memory cache for DynamoDB
- Help solve read congestion by caching
- Microseconds latency for cached data
- Doesn’t require application logic modification (compatible with existing DynamoDB APIs)
- 5 minutes TTL for cache (default)
Stream Processing
- Ordered stream of item-level modifications (create/update/delete) in a table
- Use cases:
- React to changes in real-time (welcome email to users)
- Real-time usage analytics
- Insert into derivative tables
- Implement cross-region replication
- Invoke AWS Lambda on changes to your DynamoDB table
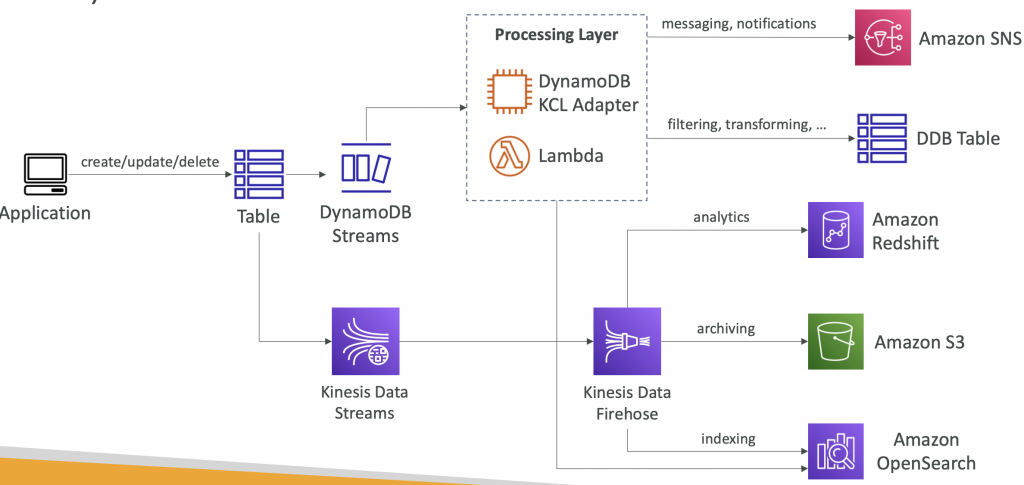
DynamoDB Streams vs Kinesis Data Streams (newer)
DynamoDB Streams
- 24 hours retention
- Limited # of consumers
- Process using AWS Lambda Triggers, or DynamoDB Stream Kinesis adapter
Kinesis Data Streams
- 1 year retention
- High # of consumers
- Process using AWS Lambda, Kinesis Data Analytics, Kineis Data Firehose, AWS Glue Streaming ETL
DynamoDB Streams
DynamoDB Global Tables
- Make a DynamoDB table accessible with low latency in multiple-regions
- Active-Active replication
- Applications can READ and WRITE to the table in any region
- Must enable DynamoDB Streams as a pre-requisite
DynamoDB –Time To Live (TTL)
- Automatically delete items after an expiry timestamp
- Use cases: reduce stored data by keeping only current items, adhere to regulatory obligations, web session handling
DynamoDB – Backups for disaster recovery
- Continuous backups using point-in-time recovery (PITR)
- Optionally enabled for the last 35 days
- Point-in-time recovery to any time within the backup window
- The recovery process creates a new table
- On-demand backups
- Full backups for long-term retention, until explicitely deleted
- Doesn’t affect performance or latency
- Can be configured and managed in AWS Backup (enables cross-region copy)
- The recovery process creates a new table
DynamoDB – Integration with Amazon S3
- Export to S3 (must enable PITR)
- Works for any point of time in the last 35 days
- Doesn’t affect the read capacity of your table
- Perform data analysis on top of DynamoDB
- Retain snapshots for auditing
- ETL on top of S3 data before importing back into DynamoDB
- Export in Dynamo DB JSON or ION format
- Import from S3
- Import CSV, DynamoDB JSON or ION format.
- Doesn’t consume any write capacity
- Creates a new table
- Import errors are logged in Cloud Watch Logs
Amazon DynamoDB – Summary
- AWS proprietary technology, managed serverless NoSQL database, millisecond latency
- Capacity modes: provisioned capacity with optional auto-scaling or on-demand capacity
- Can replace ElastiCache as a key/value store (storing session data for example, using TTL feature)
- Highly Available, Multi AZ by default, Read and Writes are decoupled, transaction capability.
- DAX cluster for read cache, microsecond read latency
- Security, authentication and authorization is done through IAM
- Event Processing: DynamoDB Streams to integrate with AWS Lambda, or Kinesis Data Streams
- Global Table feature: active-active setup
- Automated backups up to 35 days with PITR (restore to new table), or on-demand backups
- Export to S3 without using RCU within the PITR window, import from S3 with out using WCU
- Great to rapidly evolve schemas
Amazon S3 – Summary
- S3 is a… key / value store for objects
- Great for bigger objects, not so great for many small objects
- Serverless, scales infinitely, max object size is 5 TB, versioning capability
- Tiers: S3 Standard, S3 Infrequent Access, S3 Intelligent, S3 Glacier + lifecycle policy
- Features: Versioning, Encryption, Replication, MFA-Delete, Access Logs…
- Security: IAM, Bucket Policies, ACL, Access Points, Object Lambda, CORS, Object/Vault Lock • Encryption: SSE-S3, SSE-KMS, SSE-C, client-side,TLS in transit, default encryption
- Batch operations on objects using S3 Batch, listing files using S3 Inventory
- Performance: Multi-part upload, S3 Transfer Acceleration,S3 Select
- Automation: S3 Event Notifications (SNS, SQS, Lambda, EventBridge)
- Use Cases: static files, key value store for big files, website hosting
DocumentDB
- Aurora is an “AWS-implementation” of PostgreSQL / MySQL …
- DocumentDB is the same for MongoDB (which is a NoSQL database)
- MongoDB is used to store, query, and index JSON data
- Similar “deployment concepts” as Aurora
- Fully Managed, highly available with replication across 3 AZ
- DocumentDB storage automatically grows in increments of 10GB, up to 64 TB.
- Automatically scales to workloads with millions of requests per seconds
Amazon Neptune
- Fully managed graph database
- A popular graph dataset would be a social network
- Users have friends
- Posts have comments
- Comments have likes from users
- Users share and like posts…
- Highly available across 3 AZ, with up to 15 read replicas
- Build and run applications working with highly connected
- datasets – optimized for these complex and hard queries
- Can store up to billions of relations and query the graph with milliseconds latency
- Highly available with replications across multiple AZs
- Great for knowledge graphs (Wikipedia), fraud detection, recommendation engines, social networking
Amazon Keyspaces (for Apache Cassandra)
- Apache Cassandra is an open-source NoSQL distributed database
- A managed Apache Cassandra-compatible database service
- Serverless, Scalable, highly available, fully managed by AWS
- Automatically scale tables up/down based on the application’s traffic
- Tables are replicated 3 times across multiple AZ
- Using the Cassandra Query Language (CQL)
- Single-digit millisecond latency at any scale, 1000s of requests per second • Capacity: On-demand mode or provisioned mode with auto-scaling
- Encryption, backup, Point-In-Time Recovery (PITR) up to 35 days
Amazon QLDB
- QLDB stands for ”Quantum Ledger Database”
- A ledger is a book recording financial transactions
- Fully Managed, Serverless, High available, Replication across 3AZ
- Used to review history of all the changes made to your application data over time
- Immutable system: no entry can be removed or modified, cryptographically verifiable
- 2-3x better performance than common ledger blockchain frameworks, manipulate data using SQL
- Difference with Amazon Managed Blockchain: no decentralization component, in accordance with financial regulation rules
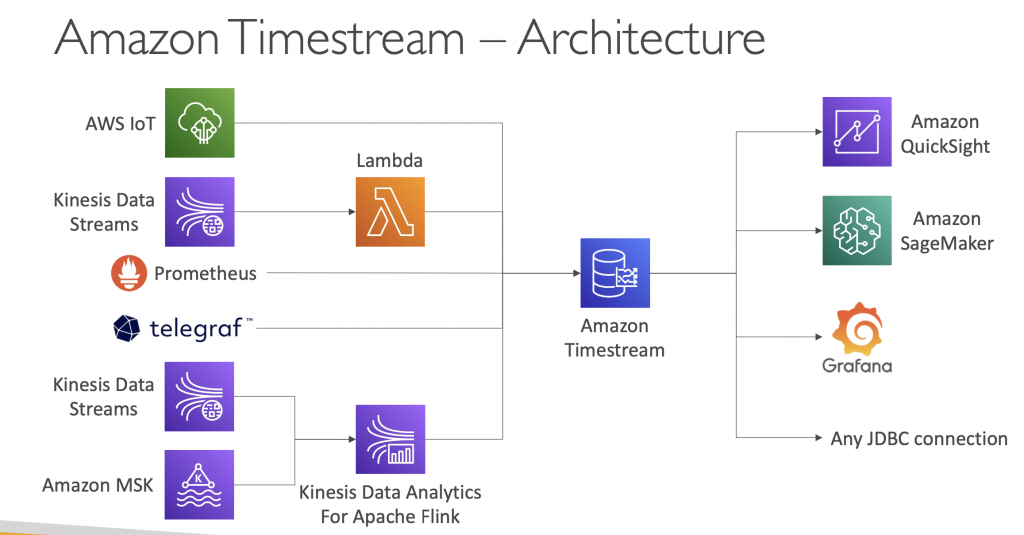
Amazon Timestream
- Fully managed, fast, scalable, serverless time series database
- Automatically scales up/down to adjust capacity
- Store and analyze trillions of events per day
- 1000s times faster & 1/10th the cost of relational databases
Scheduled queries, multi-measure records, SQL compatibility - Data storage tiering: recent data kept in memory and historical data kept in a cost-optimized storage
- Built-in time series analytics functions (helps you identify patterns in your data in near real-time)
- Encryption in transit and at rest
Redshift
- Redshift is based on PostgreSQL, but it’s not used for OLTP
- It’s OLAP – online analytical processing (analytics and data warehousing)
- 10x better performance than other data warehouses, scale to PBs of data
- Columnar storage of data (instead of row based) & parallel query engine
- Pay as you go based on the instances provisioned
- Has a SQL interface for performing the queries
- BI tools such as Amazon Quicksight or Tableau integrate with it
- vs Athena: faster queries / joins / aggregations thanks to indexes
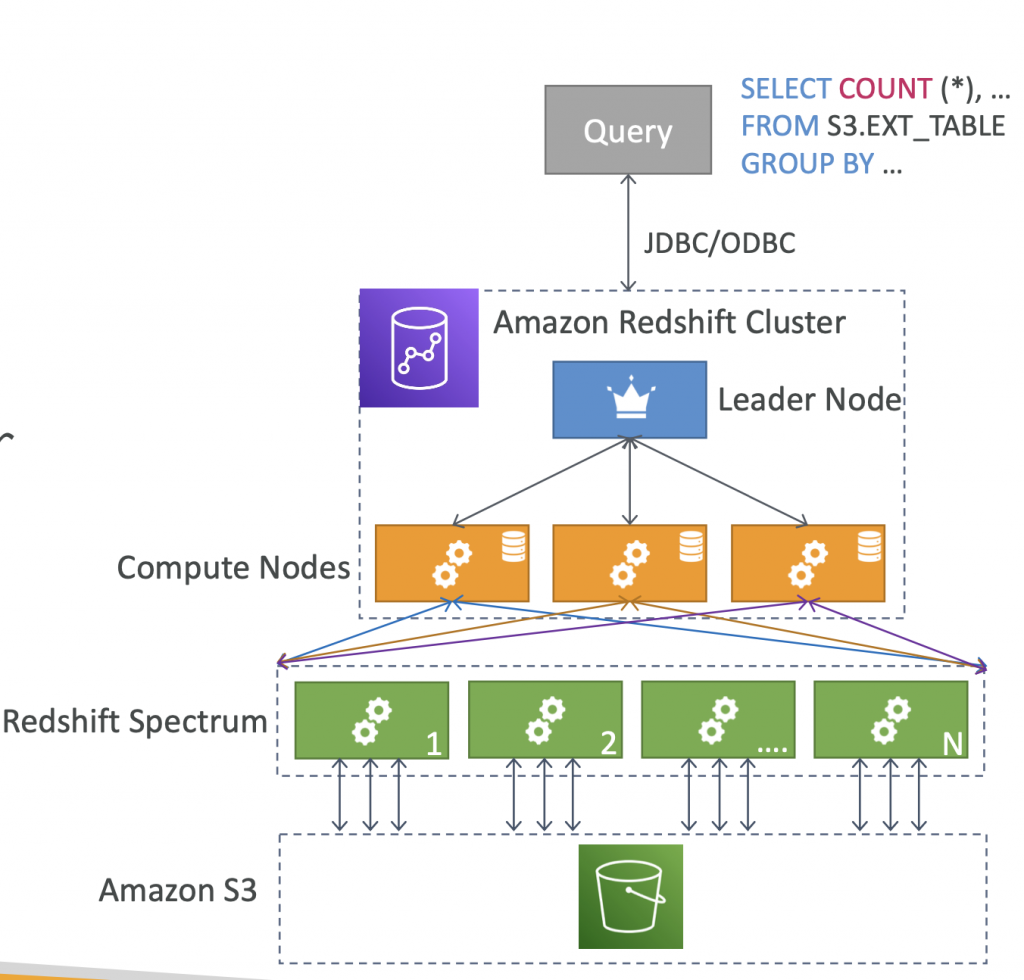
Redshift Cluster
- Leader node: for query planning, results aggregation
- Compute node: for performing the queries, send results to leader
- You provision the node size in advance
- You can used Reserved Instances for cost savings
Redshift – Snapshots & DR
- Redshift has “Multi-AZ” mode for some clusters
- Snapshots are point-in-time backups of a cluster, stored internally in S3
- Snapshots are incremental (only what has changed is saved)
- You can restore a snapshot into a new cluster
- Automated: every 8 hours, every 5 GB, or on a schedule. Set retention between 1 to 35 days
- Manual: snapshot is retained until you delete it
- You can configure Amazon Redshift to automatically copy snapshots (automated or manual) of a cluster to another AWS Region
Redshift Spectrum
- Query data that is already in S3 without loading it
- Must have a Redshift cluster available to start the query
- The query is then submitted to thousands of Redshift Spectrum nodes
Amazon OpenSearch Service
- Amazon OpenSearch is successor to Amazon ElasticSearch
- In DynamoDB, queries only exist by primary key or indexes
- With OpenSearch, you can search any field, even partially matches
- It’s common to use OpenSearch as a complement to another database
- Two modes: managed cluster or serverless cluster
- Does not natively support SQL (can be enabled via a plugin)
- Ingestion from Kinesis Data Firehose, AWS IoT, and CloudWatch Logs
- Security through Cognito & IAM, KMS encryption, TLS
- Comes with OpenSearch Dashboards (visualization)
Data Analytics
Amazon Athena
- Serverless query service to analyze data stored in Amazon S3
- Uses standard SQL language to query the files (built on Presto)
- Supports CSV, JSON, ORC, Avro, and Parquet
- Pricing: $5.00 per TB of data scanned
- Commonly used with Amazon Quicksight for repor ting/dashboards
- Use cases: Business intelligence / analytics / reporting, analyze & queryVPC Flow Logs,ELB Logs,CloudTrail trails,etc
- To analyze data in S3 using serverless SQL, use Athena
Performance Improvement Tips
- Use columnar data for cost-savings (less scan)
- Apache Parquet or ORC is recommended
- Huge performance improvement
- Use Glue to convert your data to Parquet or ORC
- Compress data for smaller retrievals (bzip2, gzip, lz4, snappy, zlip, zstd…)
- Partition datasets in S3 for easy querying on virtual columns
- Example:s3://athena-examples/flight/parquet/year=1991/month=1/day=1/
- Use larger files (> 128 MB) to minimize overhead
Amazon Athena – Federated Query
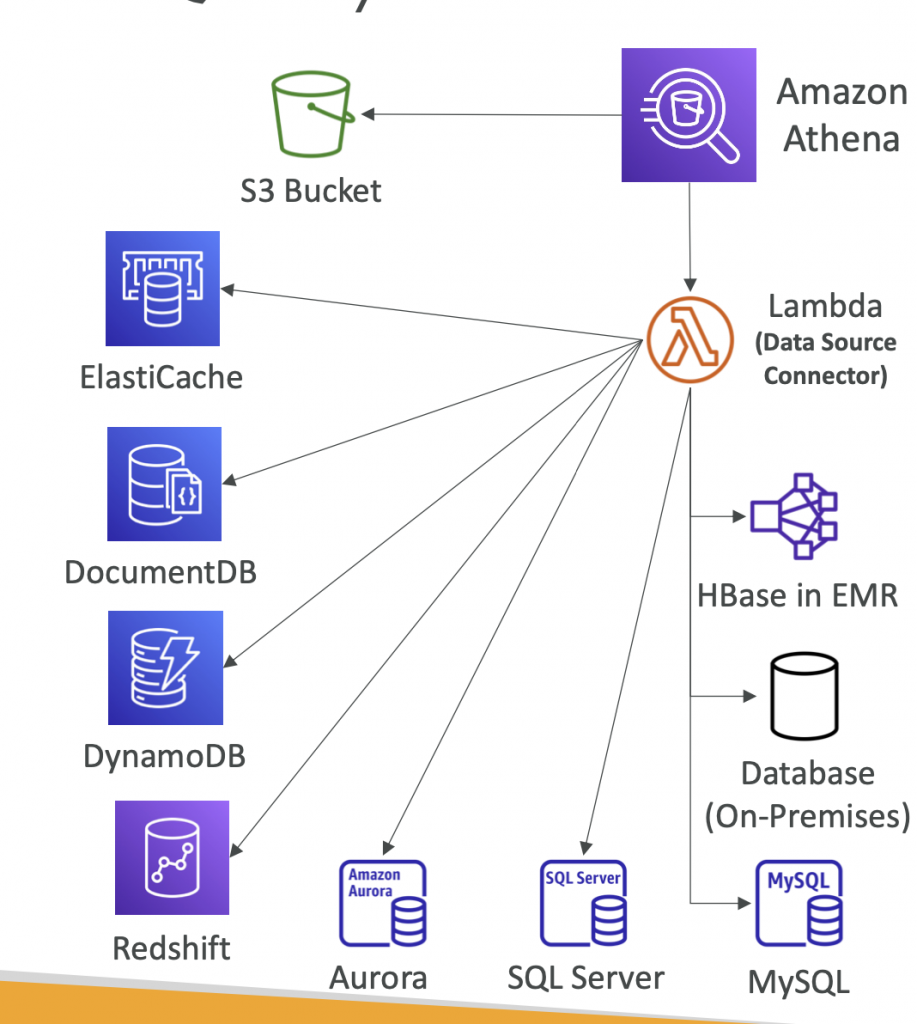
- Allows you to run SQL queries across data stored in relational, non-relational, object, and custom data sources (AWS or on-premises)
- Uses Data Source Connectors that run on AWS Lambda to run Federated Queries (e.g., CloudWatch Logs, DynamoDB, RDS, …)
- Store the results back in Amazon S3
Amazon EMR ( Elastic MapReduce
- EMR helps creating Hadoop clusters (Big Data) to analyze and process vast amount of data EMR stands for “Elastic MapReduce”
- The clusters can be made of hundreds of EC2 instances
- EMR comes bundled with Apache Spark, HBase, Presto, Flink
- EMR takes care of all the provisioning and configuration
- Auto-scaling and integrated with Spot instances
- Use cases: data processing, machine learning, web indexing, big data
- Node types
- Master Node: Manage the cluster, coordinate, manage health – long running
- Core Node: Run tasks and store data – long running
- Task Node (optional): Just to run tasks – usually Spot
- Purchasing options:
- On-demand: reliable, predictable, won’t be terminated
- Reserved (min 1 year): cost savings (EMR will automatically use if available)
- Spot Instances: cheaper, can be terminated, less reliable
- Can have long-running cluster, or transient (temporary) cluster
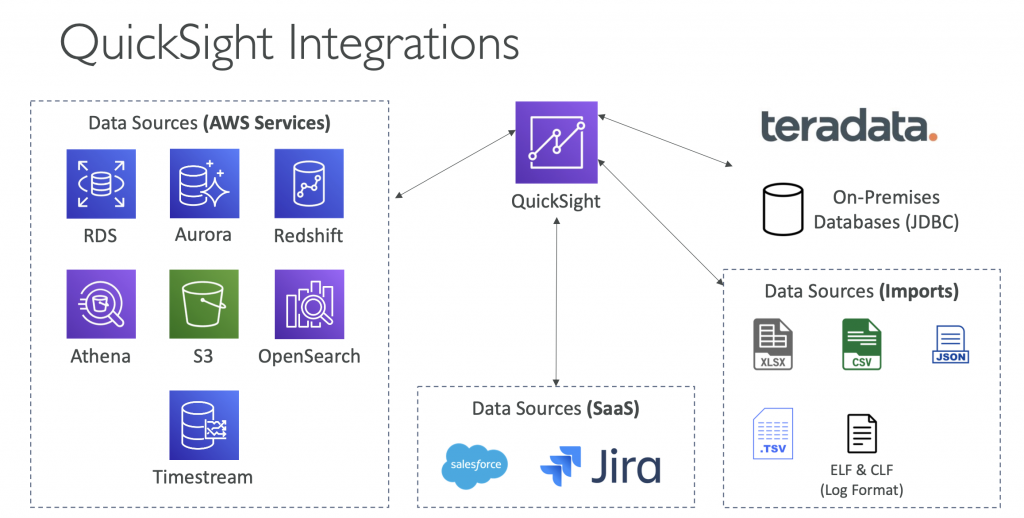
Amazon QuickSight
- Serverless machine learning-powered business intelligence service to create interactive dashboards
- Fast, automatically scalable, embeddable, with per-session pricing
- Use cases:
- Business analytics
- Building visualizations
- Perform ad-hoc analysis
- Get business insights using data
- Integrated with RDS, Aurora, Athena, Redshift, S3…
- In-memory computation using SPICE engine if data is imported into QuickSight
- Enterprise edition: Possibility to setup Column-Level security (CLS)
- Define Users (standard versions) and Groups (enterprise version)
- Define A dashboard, a read-only snapshot of an analysis that you can share, preserves the configuration of the analysis (filtering, parameters, controls, sort)
- You can share the analysis or the dashboard with Users or Groups
- To share a dashboard, you must first publish it
- Users who see the dashboard can also see the underlying data
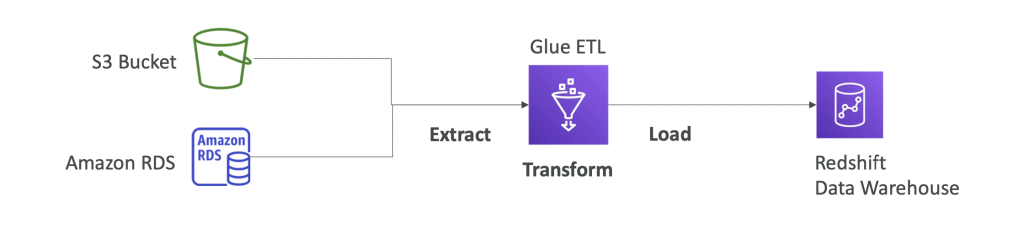
AWS Glue
- Managed extract, transform, and load (ETL) service
- Useful to prepare and transform data for analytics
- Fully serverless service
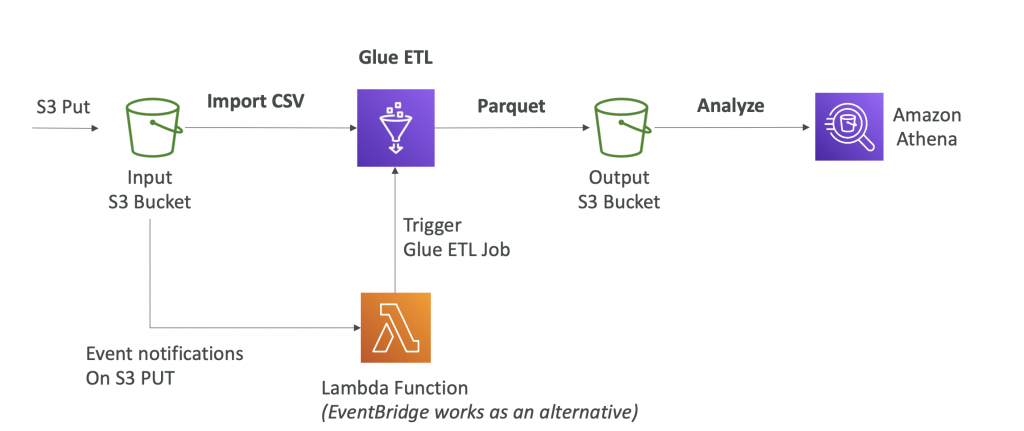
AWS Glue – Convert data into Parquet format
Glue Data Catalog: catalog of datasets
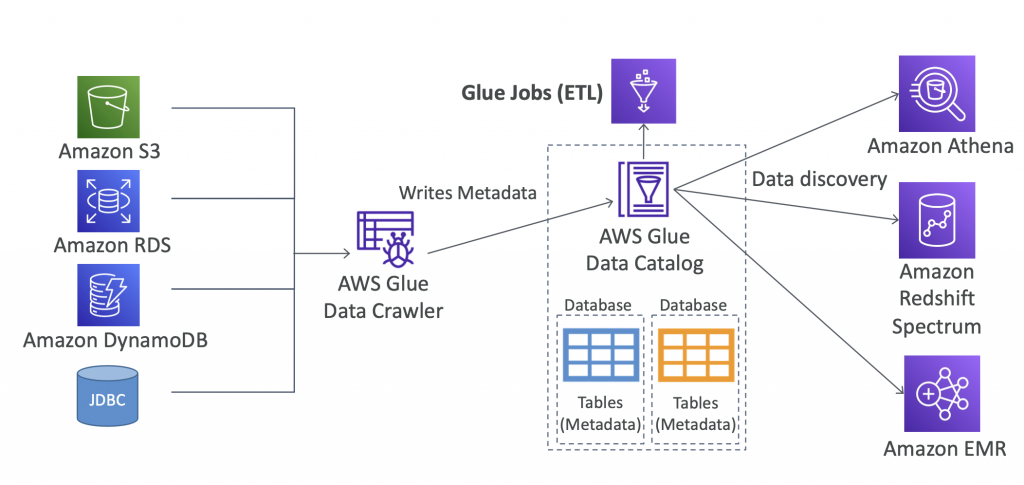
Glue Concepts
- Glue Job Bookmarks: prevent re-processing old data
- Glue Elastic Views:
- Combine and replicate data across multiple data stores using SQL
- No custom code, Glue monitors for changes in the source data, serverles
- Leverages a “virtual table” (materialized view)
- Glue DataBrew: clean and normalize data using pre-built transformation
- Glue Studio: new GUI to create, run and monitor ETL jobs in Glue
- Glue Streaming ETL (built on Apache Spark Structured Streaming): compatible with Kinesis Data Streaming, Kafka, MSK (managed Kafka)
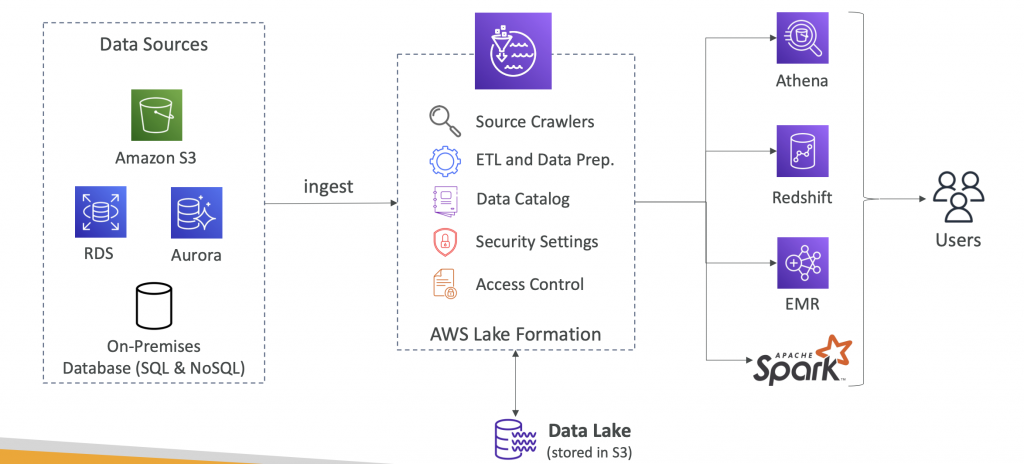
AWS Lake Formation
- Data lake = central place to have all your data for analytics purposes
- Fully managed service that makes it easy to setup a data lake in days
- Discover, cleanse, transform, and ingest data into your Data Lake
- It automates many complex manual steps (collecting, cleansing, moving, cataloging data, …) and de-duplicate (using ML Transforms)
- Combine structured and unstructured data in the data lake
- Out-of-the-box source blueprints: S3, RDS, Relational & NoSQL DB…
- Fine-grained Access Control for your applications (row and column-level)
- Built on top of AWS Glue
- Centralized Permissions
Kinesis Data Analytics
- Real-time analytics on Kinesis Data Streams & Firehose using SQL • Add reference data from Amazon S3 to enrich streaming data
- Fully managed, no servers to provision
- Automatic scaling
- Pay for actual consumption rate
- Output:
- Kinesis Data Streams: create streams out of the real-time analytics queries
- Kinesis Data Firehose: send analytics query results to destinations
- Use cases:
- Time-series analytics
- Real-time dashboards
- Real-time metrics
Kinesis Data Analytics for Apache Flink
Use Flink (Java, Scala or SQL) to process and analyze streaming data
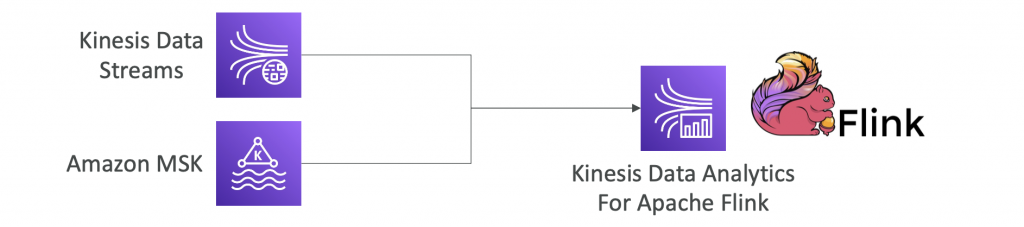
- Run any Apache Flink application on a managed cluster on AWS
- provisioning compute resources, parallel computation, automatic scaling
- application backups (implemented as checkpoints and snapshots)
- Use any Apache Flink programming features
- Flink does not read from Firehose (use Kinesis Analytics for SQL instead)
Exam Use case
Design Big Data Ingestion Pipeline
• We want the ingestion pipeline to be fully serverless
• We want to collect data in real time
• We want to transform the data
• We want to query the transformed data using SQL
• The reports created using the queries should be in S3
• We want to load that data into a warehouse and create dashboards
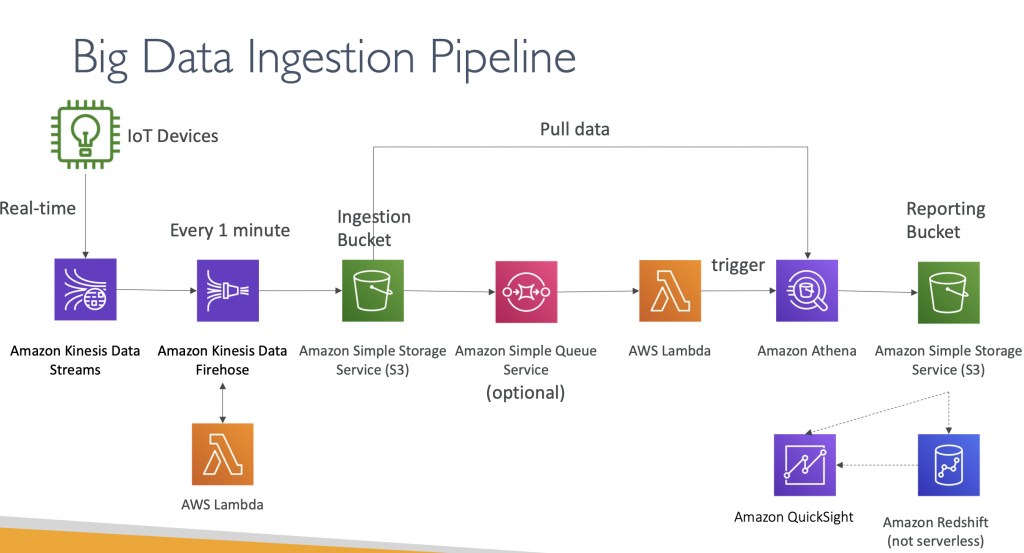
- IoT Core allows you to harvest data from IoT devices
- Kinesis is great for real-time data collection
- Firehose helps with data delivery to S3 in near real-time (1 minute)
- Lambda can help Firehose with data transformations
- Amazon S3 can trigger notifications to SQS
- Lambda can subscribe to SQS (we could have connecter S3 to Lambda)
- Athena is a serverless SQL service and results are stored in S3
- The reporting bucket contains analyzed data and can be used by reporting tool such as AWS QuickSight, Redshift, etc