This blog is a part of my journey “Embarking on the AWS Solution Architect Associate SAA-CO3 Certification Journey”
Table of Content
- Types of Encryption
- Encryption in flight
- Server side encryption at rest
- Client side encryption
- AWS KMS
- KMS Key Policies
- Copying Encrypted Snapshots across accounts
- KMS Multi-Region Keys
- SSM Parameter Store
- Standard and advanced parameter tiers
- Parameters Policies
- AWS Secrets Manager
- AWS Secrets Manager – Multi-Region Secrets
- AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- ACM – Requesting Public Certificates
- ACM – Importing Public Certificates
- ACM – Integrations
- AWS WAF – Web Application Firewall
- AWS Shield
- AWS Firewall Manager
- WAF vs. Firewall Manager vs. Shield
- Amazon GuardDuty
- Amazon Inspector
- AWS Macie
Types of Encryption
- Encryption in flight
- Data is encrypted before sending and decrypted after receiving
- SSL certificates help with encryption (HTTPS)
- Encryption in flight ensures no MITM (man in the middle attack) can happen
- Server side encryption at rest
- Data is encrypted after being received by the server
- Data is decrypted before being sent
- It is stored in an encrypted form using encryption key
- The encryption / decryption keys must be managed somewhere and the server must have access to it
- Client side encryption
- Data is encrypted by the client and never decrypted by the server
- Data will be decrypted by a receiving client
- The server should not be able to decrypt the data
AWS KMS
- Anytime you hear “encryption” for an AWS service, it’s most likely KMS
- AWS manages encryption keys for us
- Fully integrated with IAM for authorization
- Easy way to control access to your data
- Able to audit KMS Key usage using CloudTrail
- Seamlessly integrated into most AWS services
- Never ever store your secrets in plaintext, especially in your code
- Key Types
- Symmetric (AES-256 keys)
- Single encryption key that is used to Encrypt and Decrypt
- AWS services that are integrated with KMS use Symmetric CMKs
- You never get access to the KMS Key unencrypted (must call KMS API to use)
- Asymmetric (RSA & ECC key pairs)
- Public (Encrypt) and Private Key (Decrypt) pair
- Used for Encrypt/Decrypt, or Sign/Verify operations
- The public key is downloadable, but you can’t access the Private Key unencrypted
- Use case: encryption outside of AWS by users who can’t call the KMS API
- Symmetric (AES-256 keys)
- Types of KMS Keys:
- AWS Owned Keys (free): SSE-S3, SSE-SQS, SSE-DDB (default key)
- AWS Managed Key: free (aws/service-name, example: aws/rds or aws/ebs)
- Customer managed keys created in KMS: $1 / month
- Customer managed keys imported (must be symmetric key): $1 / month
- + pay for API call to KMS ($0.03 / 10000 calls)
- Automatic Key rotation:
- AWS-managed KMS Key: automatic every 1 year
- Customer-managed KMS Key: (must be enabled) automatic every 1 year
- Imported KMS Key: only manual rotation possible using alias
KMS Key Policies
- Control access to KMS keys, “similar” to S3 bucket policies
- Difference: you cannot control access without them
- Default KMS Key Policy:
- Created if you don’t provide a specific KMS Key Policy
- Complete access to the key to the root user = entire AWS account
- Custom KMS Key Policy:
- Define users, roles that can access the KMS key
- Define who can administer the key
- Useful for cross-account access of your KMS key
Copying Encrypted Snapshots across accounts
- Create a Snapshot, encrypted with your own KMS Key
- Attach a KMS Key Policy to authorize cross-account access
- Share the encrypted snapshot
- (in target) Create a copy of the Snapshot, encrypt it with a CMK in your account
- Create a volume from the snapshot

KMS Multi-Region Keys
- Identical KMS keys gets created in different AWS Regions that can be used interchangeably
- Multi-Region keys have the same key ID, key material, automatic rotation
- Encrypt in one Region and decrypt in other Regions
- No need to re-encrypt or making cross-Region API calls
- KMS Multi-Region are NOT global (Primary + Replicas)
- Each Multi-Region key is managed independently
- Use cases: global client-side encryption, encryption on Global DynamoDB, Global Aurora
- Integration with
- Global DynamoDB to encrypt specific attribute globally
- We can encrypt specific attributes client-side in our Aurora table
- S3 Replication
- Unencrypted objects and objects encrypted with SSE-S3 are replicated by default
- Objects encrypted with SSE-C (customer provided key) are never replicated
- For objects encrypted with SSE-KMS, you need to enable the option
- Specify which KMS Key to encrypt the objects within the target bucket
- Adapt the KMS Key Policy for the target key
- An IAM Role with kms:Decrypt for the source KMS Key and kms:Encrypt for the target KMS Key
- You might get KMS throttling errors, in which case you can ask for a Service Quotas increase
- You can use multi-region AWS KMS Keys, but they are currently treated as independent keys by Amazon S3
- AMI Sharing Process Encrypted via KMS
SSM Parameter Store
- Secure storage for configuration and secrets
- Optional Seamless Encryption using KMS
- Serverless, scalable, durable, easy SDK
- Version tracking of configurations / secrets
- Security through IAM
- Notifications with Amazon EventBridge
- Integration with CloudFormation
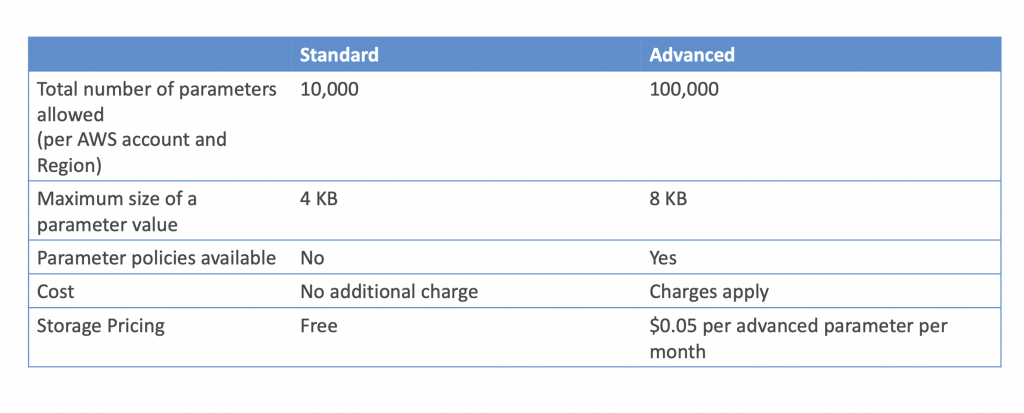
Standard and advanced parameter tiers
Parameters Policies
- Allow to assign a TTL to a parameter (expiration date) to force updating or deleting sensitive data such as passwords
- Can assign multiple policies at a time
AWS Secrets Manager
- Newer service, meant for storing secrets
- Capability to force rotation of secrets every X days
- Automate generation of secrets on rotation (uses Lambda)
- Integration with Amazon RDS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Aurora)
- Secrets are encrypted using KMS
- Mostly meant for RDS integration
AWS Secrets Manager – Multi-Region Secrets
- Replicate Secrets across multiple AWS Regions
- Secrets Manager keeps read replicas in sync with the primary Secret
- Ability to promote a read replica Secret to a standalone Secret
- Use cases: multi-region apps, disaster recovery strategies, multi-region DB
AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- Easily provision, manage, and deploy TLS Certificates
- Provide in-flight encryption for websites
- Supports both public and privateTLS certificates
- Free of charge for publicTLS certificates
- AutomaticTLS certificate renewal
- Integrations with (loadTLS certificates on)
- Elastic Load Balancers(CLB,ALB,NLB)
- CloudFront Distributions
- APIs on API Gateway
- Cannot use ACM with EC2
ACM – Requesting Public Certificates
- List domain names to be included in the certificate
- Fully Qualified Domain Name
- WildcardDomain:*.example.com
- Select Validation Method: DNS Validation or Email validation
- DNS Validation is preferred for automation purposes
- Email validation will send emails to contact addresses in the WHOIS database
- DNS Validation will leverage a CNAME record to DNS config
- It will take a few hours to get verified
- The Public Certificate will be enrolled for automatic renewal
- ACM automatically renews ACM-generated certificates 60 days before expiry
ACM – Importing Public Certificates
- Option to generate the certificate outside of ACM and then import it
- No automatic renewal, must import a new certificate before expiry
- ACM sends daily expiration event starting 45 days prior to expiration
- The # of days can be configured
- Events are appearing in EventBridge
- AWS Config has a managed rule named acm-certificate-expiration-check to check for expiring certificates
ACM – Integrations
- ALB
- AWS Gateway
- Edge-Optimized (default): For global clients
- Requests are routed through the CloudFront Edge locations
- The API Gateway still lives in only one region
- The TLS Certificate must be in the same region as CloudFront, in us-east-1
- Then setup CNAME or (better) A-Alias record in Route53
- Regional
- For clients within the same region
- The TLS Certificate must be imported on API Gateway, in the same region as the API Stage
- ThensetupCNAMEor(better)A-AliasrecordinRoute53
- Edge-Optimized (default): For global clients
AWS WAF – Web Application Firewall
- Protects your web applications from common web exploits (Layer 7)
- Layer 7 is HTTP (vs Layer 4 is TCP/UDP)
- Deploy on
- Application Load Balancer
- API Gateway
- CloudFront
- AppSync GraphQL API
- Define Web ACL (Web Access Control List) Rules:
- IP Set: up to 10,000 IP addresses – use multiple Rules for more IPs
- HTTP headers, HTTP body, or URI strings Protects from common attack – SQL injection and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Size constraints, geo-match (block countries)
- Rate-based rules (to count occurrences of events) – for DDoS protection
- Web ACL are Regional except for CloudFron
- A rule group is a reusable set of rules that you can add to a web ACL
AWS Shield
- AWS Shield Standard:
- Free service that is activated for every AWS customer
- Provides protection from attacks such as SYN/UDP Floods, Reflection attacks and other layer 3/ 4 attacks.
- AWS Shield Advanced
- Optional DDoS mitigation service ($3,000 per month per organization)
- Protect against more sophisticated attack on Amazon EC2, Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), Amazon CloudFront, AWS Global Accelerator, and Route 53
- 24/7 access to AWS DDoS response team (DRP)
- Protect against higher fees during usage spikes due to DDoS
- Shield Advanced automatic application layer DDoS mitigation automatically creates, evaluates and deploys AWS WAF rules to mitigate layer 7 attacks
AWS Firewall Manager
- Manage rules in all accounts of an AWS Organization
- Security policy: common set of security rules
- WAF rules (Application Load Balancer, API Gateways, CloudFront)
- AWS Shield Advanced (ALB, CLB, NLB, Elastic IP, CloudFront)
- Security Groups for EC2, Application Load BAlancer and ENI resources in VPC
- AWS Network Firewall (VPC Level)
- Amazon Route 53 Resolver DNS Firewall
- Policies are created at the region level
- Rules are applied to new resources as they are created (good for compliance) across all and future accounts in your Organization
WAF vs. Firewall Manager vs. Shield
- WAF, Shield and Firewall Manager are used together for comprehensive protection
- Define your Web ACL rules in WAF
- For granular protection of your resources,WAF alone is the correct choice
- If you want to use AWS WAF across accounts, accelerate WAF configuration, automate the protection of new resources, use Firewall Manager with AWS WAF
- Shield Advanced adds additional features on top of AWS WAF, such as dedicated suppor t from the Shield ResponseTeam (SRT) and advanced reporting.
- If you’re prone to frequent DDoS attacks, consider purchasing Shield Advanced
Amazon GuardDuty
- Intelligent Threat discovery to protect your AWS Account
- Uses Machine Learning algorithms, anomaly detection, 3rd party data
- One click to enable (30 days trial), no need to install software
- Input data includes:
- CloudTrail Events Logs – unusual API calls, unauthorized deployments
- VPC Flow Logs – unusual internal traffic, unusual IP address
- DNS Logs – compromised EC2 instances sending encoded data within DNS queries
- Optional Features – EKS Audit Logs, RDS & Aurora, EBS, Lambda, S3 Data Events
- Can setup EventBridge rules to be notified in case of findings
- EventBridge rules can target AWS Lambda or SNS
- Can protect against CryptoCurrency attacks
Amazon Inspector
- Automated Security Assessments
- Supports
- EC2
- Leveraging the AWS System Manager (SSM) agent
- Analyze against unintended network accessibility
- Analyze the running OS against known vulnerabilities
- Amazon ECR
- Assessment of Container Images as they are pushed
- Lambda Functions
- Identifies software vulnerabilities in function code and package dependencies
- Assessment of functions as they are deployed
- EC2
- Reporting & integration with AWS Security Hub
- Send findings to Amazon Event Bridge
- Inspector does following this
- Continuous scanning of the infrastructure, only when needed
- Package vulnerabilities (EC2, ECR & Lambda) – database of CVE
- Network reachability (EC2)
- A risk score is associated with all vulnerabilities for prioritization
AWS Macie
- Amazon Macie is a fully managed data security and data privacy service that uses machine learning and pattern matching to discover and protect your sensitive data in AWS
- Macie helps identify and alert you to sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII)