The database is used to store data and help us to query complex queries. As time passes every table becomes heavy the number of rows a particular table will increase. This will lead to a slow response of queried data. Indexing addresses this problem, what essentially an index does is sort the data in such a way that it becomes easy to find a row in the table. Indexes are applied on columns so when we query for data using the column we will get data quickly.
For example consider we have a student table, with roll_number, and name. If we have indexed column roll_number. Queries that depends on roll_number will be executed fast
select * from students where roll_number = 37;Types of Indexes.
I have faced this question frequently in interviews. Tell me about types of indexes, so now you will know the answer to that question. There are majorly 2 types of indexes.
Primary Index or clustered Index.
In the end no matter what you see in a database table, rows, etc. The data are stored on hard drives, they may or may not be stored sequentially.
In the Primary index case, the data is stored in a sorted format on the hard drive. Consider the above case, for the student’s table. The data is stored in sorted form as per the roll_number.
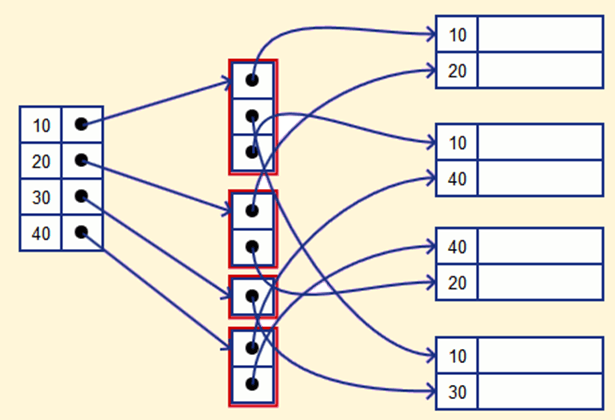
Secondary Index
In the case of a secondary index, if we have a secondary index on a column the database creates a new data structure to store the data of that column in sorted order without doing any changes to the physical storage format.
I request to go through this article for in-depth detail for this concept. https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/database-indexing-at-a-glance-bb50809d48bd/